QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions below:
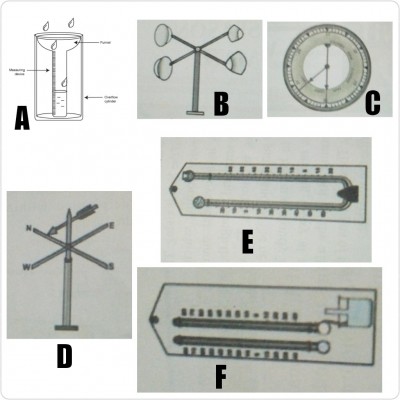
a) Identify A, B, C, D, E and F.
ANS: A-Rain gauge
B-Anemometer
C-Barometer
D-Wind vane
E-Maximum and minimum thermometer
F-Wet and dry bulb hygrometer
a) State the use of A, B, C, D, E and F.
ANS:
A-For measuring the amount of rainfall
B-For measuring the speed of wind
C-For measuring atmospheric pressure
D-For measuring the direction of wind.
E-For measuring temperature of an area.
F-For measuring humidity of the atmosphere
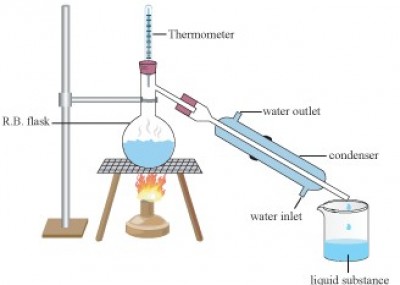
The diagram is an illustration of an experimental set-up used for separating a mixture of water and alcohol.
a) Name the method of separation of the mixture.
ANS: Simple distillation
b) A liquid substance was formed in the beaker when the mixture was heated at 78°C. What is the liquid substance?
ANS: Alcohol(ethanol)
c) Name the substance that remains in the flask after 78°C.
ANS: Water
d) State the function of the thermometer and the condenser.
ANS: Thermometer is used to measure the temperature at which the mixture boils while the condenser is used to cool the vapour.
e) What is the other name of the condenser?
ANS: Water jacket
f) Name the physical processes that are involved in the method of separation of the mixture.
ANS: Heating, vaporization, condensation.
g) Why was the alcohol separated first?
ANS: Because it has a lower boiling point than water.
h) Name one example of a mixture that can be separated by the method illustrated.
ANS: Water and acetone
I) State two applications of the method of separation illustrated.
ANS: 1. Local preparation of akpeteshie
2. Purification of water
3. Separation of components of crude oil.
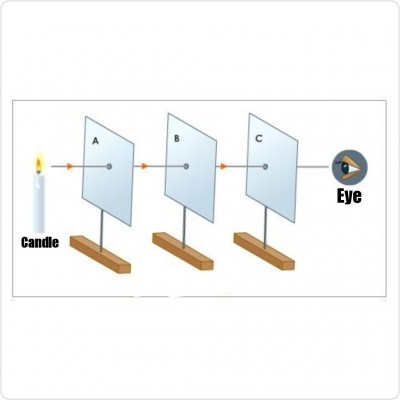
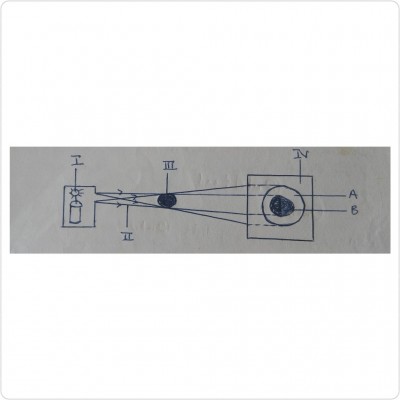
Use the diagram illustrated to answer the questions below:
a) What would the observer see from the position shown?
ANS: The observer will see light rays.
b) What happens when cardboard B is shifted?
ANS: Light can no longer be seen through the holes
c) Explain the observation made in (b) above.
ANS: Light travels in straight line and because cardboard B is shifted out of the straight line, the light is not seen again.
d) What does the experiment demonstrate?
ANS: It demonstrates that light travels in straight line.
e) Mention two devices that work on the property of light demonstrated.
ANS: Pinhole camera, torchlight, periscope.
f) Mention two natural occurrences that could be explained by the property of light demonstrated.
ANS: Formation of shadows and eclipses.
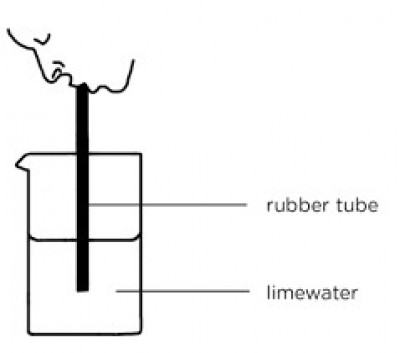
The set-up illustrated shows air breathed out through the mouth into a test tube containing lime water.
a) What observation would be made after some time?
ANS: Lime water turns milky
b) Explain the observation made above.
ANS: Breathed out air contains carbon dioxide which turns the lime water milky.
c) Identify the milky substance produced.
ANS: Calcium carbonate
d) Name two other substances present in breathed-out air.
ANS: Nitrogen, water vapour, unused oxygen.
e) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
ANS: Ca(OH)2 + CO2------> CaCO3 + H2O
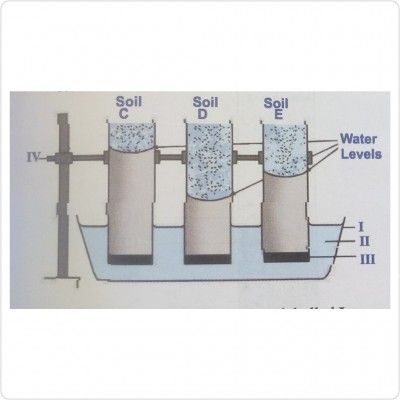
The diagram is an illustration of the experimental set-up to compare capillary action in sand, Loam and clay.
a) Name the parts of the set-up labelled I, II, III and IV.
ANS: I-Water trough
II-Water
III-Cotton wool
IV-Retort stand and clamp
b) From the results indicated in the diagram, identify the soil types C, D and E.
ANS: Soil C-Clay
Soil D-Water
Soil E-Loam
c) Which of the soil types has the least capillary action?
AND: Soil D
d) Which of the soil types is most suitable for growing garden eggs?
ANS: Soil E
e) State two precautions that should be observed during the demonstration.
ANS: 1. Dry soil samples should be used.
2. Glass tubes with the same diameter should be used.
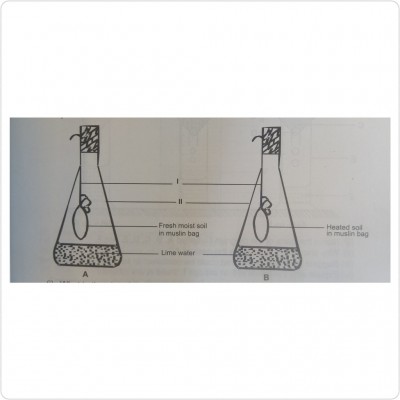
Study the experimental set-up shown and use it to answer the questions below:
a) What is the aim of the experiment?
ANS: To demonstrate that living organisms are present in the soil.
b) Name the parts of the set-up labelled I and II.
ANS: I-Thread/string
II-Conical flask
c) What observation could be made about the lime water in A after six hours?
ANS: The lime water turns milky.
d) Explain the observation made in (c).
ANS: The fresh moist soil contains living organisms which respire, giving out carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide released caused the lime water to turn milky.
e) What would be the observation in B after six hours?
ANS: Lime water remains the same. This is because there is no living organism in soil B to respire due to heating of soil.
'C' is a list of tools used in performing the functions in list 'D'. From list 'C', choose the correct tool you would use to perform each of the functions in list 'D' and write down your answers in the spaces provided.
'C'
Handfork. Pick axe. Hoe
Shears. Hand trowel. Dibber
ANSWERS;
i) Hoe
ii) Hand trowel
iii) Shears
iv) Hand fork
v) Pick axe
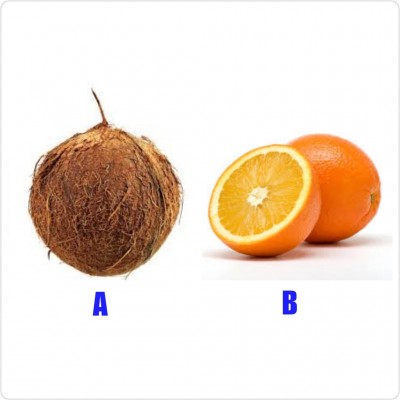
The diagrams shown are illustrations of some fruits labelled A and B.
a) Name each of the fruits A and B.
ANS: A-Coconut. B-Orange
b) State the type of fruit represented each by A and B.
ANS: A-Drupes. B-Berries
c) Which part of the flower develops into the fruits illustrated?
ANS: Ovary
d) State one feature each that enables fruit A and B to be dispersed.
ANS: A-Has a lower density so can float on water.
B-It is juicy and fleshy with sweet scent.
e) State one difference between fruit A and B.
ANS: A has one seed while B has many seeds.
f) Name the two processes that results in the formation of the fruits shown.
ANS: Pollination and fertilization
The diagram shows the formation of shadows. Use it to answer the questions below:
a) State the type of shadows labelled A and B.
ANS: A-Penumbra. B-Umbra
b) Name the parts labelled I, II, III and IV.
ANS: I-Light source
II-Light rays
III-Opaque object
IV-Screen
c) Which of the parts was used to cast the shadow?
ANS: Part III
d) Which law of light energy does the experiment demonstrate?
ANS: Rectilinear propagation of light
e) State a natural phenomenon that can represent the diagram illustrated.
ANS: Eclipse
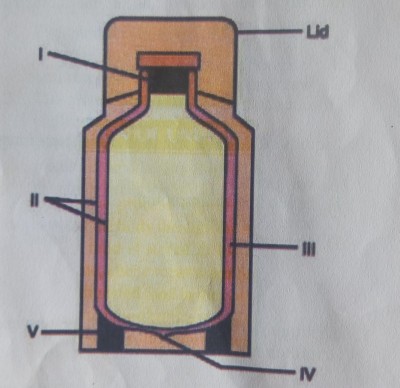
Use the diagram to answer the questions below:
a) Identify the figure illustrated.
ANS: Vacuum flask
b) Name the parts labelled I, II, III, IV and V.
ANS: I-Cork or plastic stopper.
II-Doubled-walled and silvered glass container.
III-Vacuum
IV-Vacuum seal
V-Cork support
c) State the use of the figure.
ANS: It is used to store both cold and hot items.
d) State the function of parts labelled I and III.
ANS: I-It prevents heat loss or heat gain by conduction.
III-It prevents heat loss or heat gain by conduction and convection.
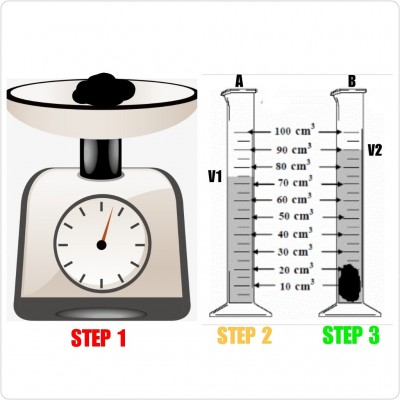
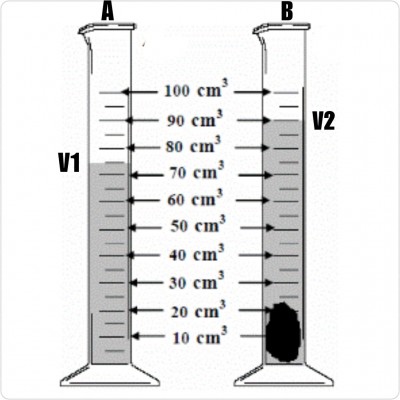
The diagrams show how pupils of African Unity J. H. S determined the density of a piece of stone.
a) Name the apparatus used in step 1 and step 2.
ANS: Step 1-Weighing balance
Step 2-Measuring cylinder
b) Describe briefly each of the three steps.
ANS: Step 1-A balance was used to measure the mass of the stone.
Step 2-Water was poured into the measuring cylinder and the initial volume is read and recorded.
Step 3-A stone was lowered gently into the water in the measuring cylinder and the final volume is read and recorded.
c) What is the initial volume V1 of the water?
ANS: V1=75cm³
d) What is the final volume V2 of the water?
ANS: V2=90cm³
e) Calculate the volume of the stone.
ANS: Volume = V2 - V1
= 90cm³ - 75cm³
= 20cm³
f) Name two other instruments for measuring volume of liquids.
ANS: Beaker, pipette, burette.
g) If the mass of the stone is 60g, determine the density of the stone.
ANS: Density = mass/volume
= 60g/20cm³
= 3g/cm³
The set-up illustrated was used to demonstrate an activity. Study it carefully and answer the questions below:
a) Suggest a suitable title for the experiment.
ANS: Finding the volume of irregular objects.
b) Name the instrument used in the experiment.
ANS: Measuring cylinder
c) What is the initial volume V1 of the water?
ANS: Initial volume V1=75cm³
d) What is the final volume V2 of the water?
ANS: Final volume V2=90cm³
e) Calculate the volume of the stone.
ANS: Volume = V2 - V1
= 90cm³-75cm³
= 20cm³
f) Name one other instrument that could be used to determine the volume of the stone.
ANS: Overflow or Eureka can, graduated beaker.
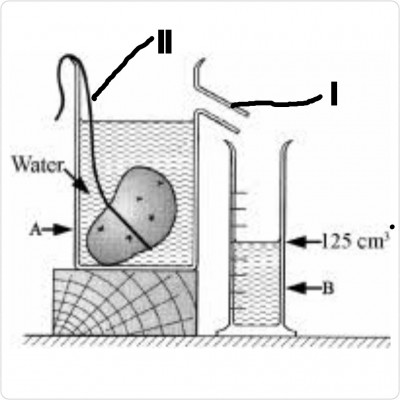
A pupil measured the volume of potato using the laboratory equipments labelled A and B as shown. The potato had a mass of 250g.
a) Name the equipments labelled A and B.
ANS: A-Eureka can
B-Measuring cylinder
b) Name the parts labelled I and II.
ANS: I-Spout
II-Thread/String
c) What is the volume of the potato?
ANS: Volume =125cm³
d) Name the instrument that can be used to measure the mass of the potato.
ANS: Weighing balance or beam balance
e) Calculate the density of the potato.
ANS: Density = mass/volume
= 250g / 125cm³
= 2g/cm³
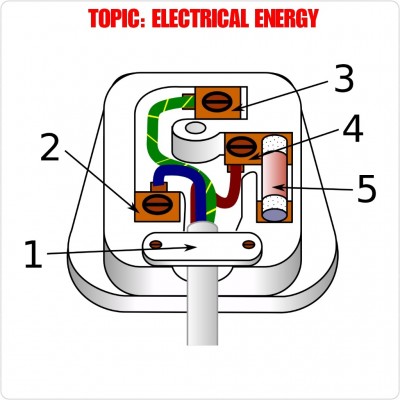
Use the diagram to answer the questions below:
a) Name the diagram.
ANS: A three-pin plug
b) What name is given to each of the wires with the following colours in the diagram;
i. blue. ii. green and yellow
iii. brown
ANS: i. neutral wire
ii. earth wire
iii. live wire
c) Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
ANS: 1-Cable grip
2-Neutral terminal
3-Earth terminal
4-Live terminal
5-Fuse
d) Which of the parts labelled is used to prevent fires?
ANS: Part 5(fuse)