QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
TOPIC:DENTITION IN HUMANS
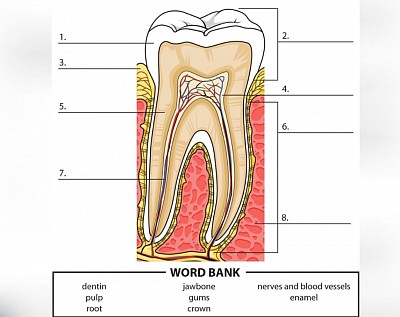
Study the structure above and answer the questions below :
(a) Which of the parts labelled form the crown?
ans:
(b) Identify the parts labelled 1 to
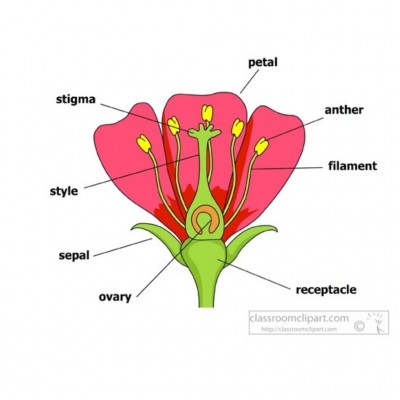
Study the structure carefully and answer the questions that follow :
a) Identify the structure.
ans: A flower
b) State one function each of stigma, anther, petal and sepal.
ans: *Stigma-It receives pollen grains during pollination.
*Anther-It produces or contains the pollen grains.
*Petal-It attracts insects and birds for pollination.
*Sepal-It protects the flower at the bud stage.
c) What is the collective name given to the anther and filament?
ans: Stamen
d) What is the collective name given to stigma, style, ovary and ovule?
ans: Pistil or carpel
e) State two changes that occur in a flower after fertilization.
ans: 1. Ovules become the seed.
2. Ovary become the fruit.
#READY_4_EXAMS
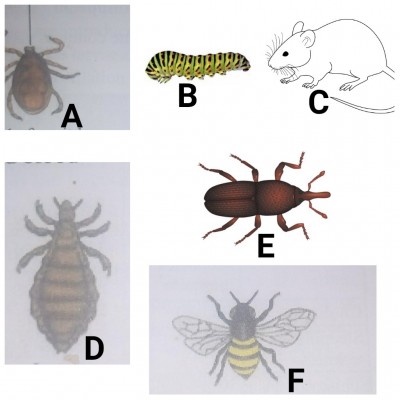
Study the living organisms illustrated and answer the questions that follow :
a) Identify each of the living organisms labelled A, B, C, D, E and F.
ans: A-Tick
B-Caterpillar
C-Mouse/Rat
D-Louse
E-Weevil
F-Tsetsefly
b) Which of the organisms are pests?
ans: Organisms C, B and E.
c) Which of the organisms are parasites?
ans: Organisms A, D and F.
d) List four crops which are attacked by the organisms named in (b) above.
ans: Yam, cassava, rice, maize, groundnut, tomatoes, etc.
e) State one effect each of organism A and D on living organisms.
ans: A-It sucks blood from dogs, sheep, etc
D-It sucks blood from humans leading to anaemia.
f) State three methods of controlling organism C.
ans: 1. Weed control.
2. Early harvesting.
3. Application of recommended pesticides.
4. Setting traps.
5. Proper fencing.
#READY_4_EXAMS
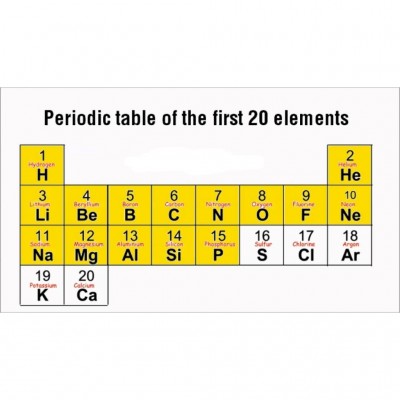
The table represents the first 20 elements of the periodic table.
a) By what principle are elements arranged on the periodic table?
ans: According to their increasing atomic numbers.
b) Which group on the periodic table represents metals?
ans: Group 1-3
c) Which group on the periodic table represents non-metals?
ans: Group 4-8
d) Which group represents the most reactive metals?
ans: Group 1
e) Which group represents the most reactive non-metals?
ans: Group 7
f) Name the two elements on the periodic table that are metalloids.
ans: Boron and Silicon
g) Name the most reactive metal on the periodic table.
ans: Potassium
h) Name two elements on the periodic table that belong to group 5.
ans: Nitrogen and Phosphorus
I) Name two elements on the periodic table that belong to period 3.
ans: Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminum, Silicon, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Chlorine, Argon.
j) List any two alkali metals from the table.
ans: Lithium, Sodium, Potassium.
#READY_4_EXAMS
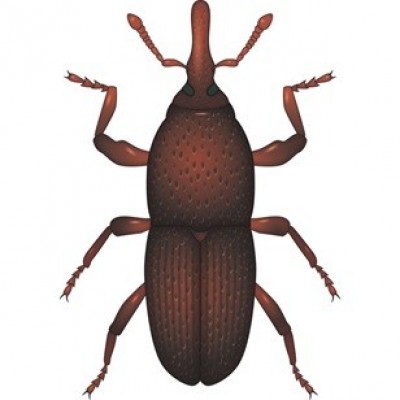
Study the organism illustrated carefully and answer the questions that follow :
a) Identify the organism illustrated.
ans: Weevil
b) State whether the organism is a pest or parasite.
ans: Pest
c) Name two food crops that are mostly attacked by the organism.
ans: Maize, rice, beans, etc.
d) Name three other examples of the answer given in (b) above.
ans: Caterpillar, Rat, Squirrel, etc.
e) State two effects of the organism on crops.
ans: 1. It reduces crop yield.
2. It exposes crops to diseases.
#READY_4_EXAMS
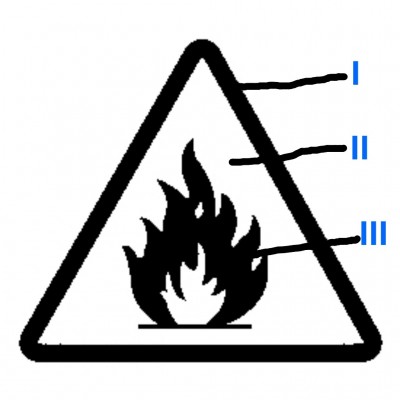
The diagram illustrates a hazard symbol. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow :
a) What does the symbol represent?
ans: Highly flammable
b) Name two substances that is associated with the symbol.
ans: Petrol, LPG, ethanol(alcohol), gasoline, etc.
c) Name a place where the hazard symbol is often displayed.
ans: LPG station, Petrol filling station.
d) What type of safety sign is the diagram?
ans: Warning safety sign
e) Name two safety devices that can be used to control the hazard symbol.
ans: Fire extinguisher, fire alarm, fire blanket, sand bucket, etc.
f) What colour is represented by parts labelled I, II and III?
ans: I-Black
II-Yellow
III-Black
#READY_4_EXAMS
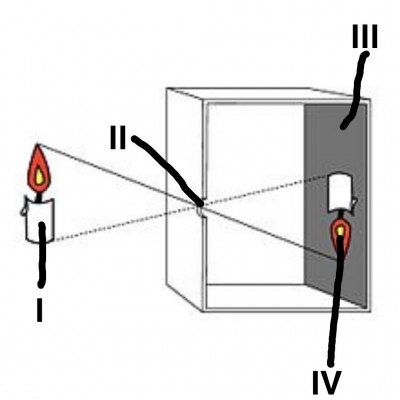
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow :
a) Identify the above set-up.
ans: Pinhole camera
b) Label the parts I, II, III and IV.
ans: I-Object
II-Pinhole
III-Screen
IV-Image
c) State two characteristics of images formed by the set-up.
ans: 1. It is real.
2. It is inverted.
3. It is diminished.
d) Explain why the part labelled IV is inverted?
ans: Because light rays traveling in straight lines from the top and bottom of I intersect at II.
e) Name two materials that can be used to construct the set-up.
ans: Cardboard, frosted glass.
#READY_4_EXAMS
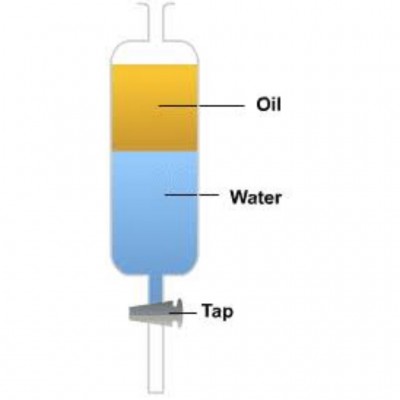
The diagram shows the set-up used to separate a mixture. Study it carefully and answer the questions below :
a) What method of separation is used in the set-up?
ans: Separating funnel method
b) Name the two apparatus used in the set-up.
ans: Separating funnel, retort stand and clamp.
c) State the physical property of the components of the mixture that makes thier separation possible.
ans: Density
d) What name is given to the type of mixture being separated?
ans: Immiscible liquid mixture.
e) Name one other example of a mixture that could be separated by the set-up.
ans: Kerosene and water.
#READY_4_EXAMS
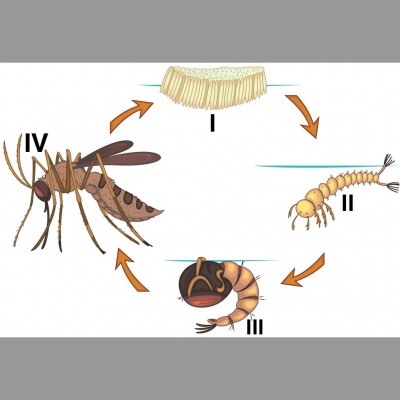
The diagram illustrated shows the life cycle of a living organism.
a) What life cycle does the diagram represent?
ans: The life cycle of a mosquito.
b) Name the parts of the cycle labelled I, II, III and IV.
ans: I-Egg
II-Larva
III-Pupa
IV-Adult mosquito
c) Name four methods that can be used to control part IV.
ans: 1. Environmental method
2. Chemical method
3. Biological method
4. Genetic method
d) Mention two places where the cycle is likely to be found.
ans: Stagnant pool of water, empty cans, choked gutters, etc
e) Name the parasite transmitted by part labelled IV.
ans: Plasmodium
f) Name the three common groups of part labelled IV.
ans: Added, Culex, Anopheles.
g) How many days does the cycle above lasts?
ans: 28 days
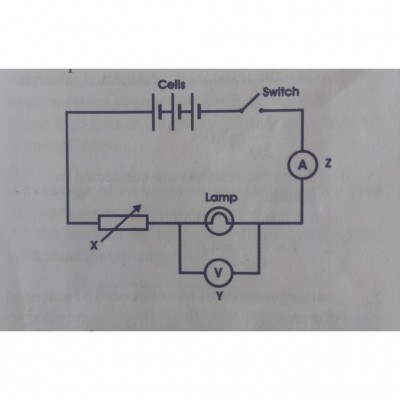
Study the circuit diagram and answer the questions that follow :
(a) Name the components X, Y and Z.
ans: X-Rheostat
Y-Voltmeter
Z-Ammeter
(b) What effect would a reduction in the number of cells have on:
i) the current in the circuit.
ii) the voltage.
ans: i) The current of the circuit would reduce.
ii) The voltage would reduce.
(c) State two changes in the circuit that would increase the brightness of the lamp.
ans: 1. By increasing the number of cells.
2. By decreasing the resistance of the variable resistor.
(d) Calculate the total emf of the cells if each is 2.0V.
ans: Total emf= E1 + E2 + E3
= 2.0 +2.0 + 2.0
= 6V
(e) State the function of the switch in the circuit.
ans: It is used to open and close the circuit.
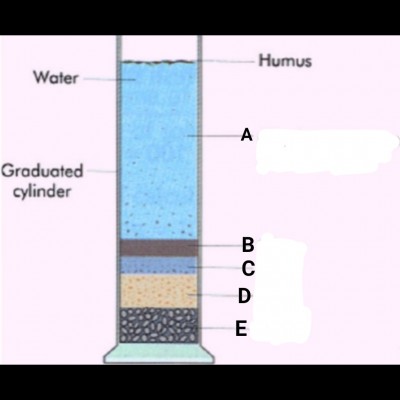
The diagram above is an illustration of a sample of garden soil put in a cylinder containing water. It was shaken and allowed to settle.
(a) State the aim of the experimental set-up.
ANS: To show that soil is made up of different sized particles.
(b) Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D and E.
ANS: A-Clay suspension
B-Clay
C-Silt
D-Sand
E-Gravel
(c) Mention the physical property of the soil that could be determined from the experiment.
ANS: Soil texture
(d) Outline three importance of humus in crop production.
ANS: 1. It improves soil structure.
2. It improves soil fertility.
3. It improves soil aeration.
(e) What conclusion could be drawn from the experiment?
ANS:
Soil is made up of different sized particles.
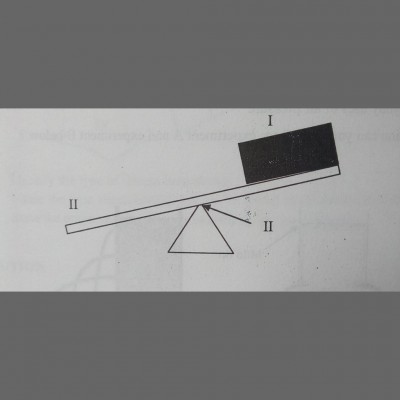
The diagram represents a simple machine. Use it to answer the questions below if the load is 20N and the effort is 25N.
(a) Identify and define the load, pivot and effort.
ANS: I-load; it is the force that the effort overcomes
II-pivot; it is the turning point of a lever
III-effort; it is the force applied to the machine
(b) Which class of simple machine is illustrated?
ANS: First Class lever
(c) If the load distance is 0.024m and the effort distance is 0.039m, calculate
(i) Mechanical advantage
(ii) Velocity ratio
(iii) Efficiency of the machine
ANS: i) M. A=load ÷effort
=20N÷25N
=0.8
ii) V. R=effort dist.÷load dist.
=0.039÷0.024
=1.625
iii) Efficiency =(M. A/V.R)×100
=(0.8÷1.625)×100
=49.23%
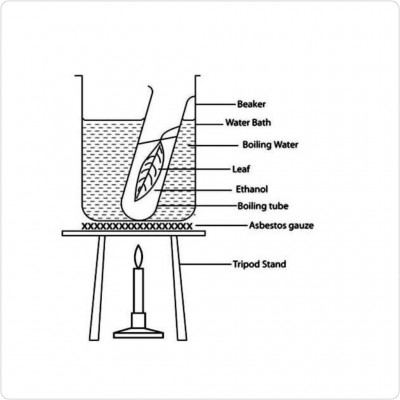
Study the diagram which shows an aspect of photosynthesis and answer the questions below:
a) State the aim of the experiment.
ANS: To show that starch is present in green leaves.
b) Give the function of the ethanol in the experiment.
ANS: To remove the chlorophyll from the leaf.
c) State one reason why the green leaf should be boiled in water first.
ANS: To kill the cells of the leaf
d) Mention two reasons why the green leaf after being removed from the ethanol should be washed with warm water.
ANS: 1. To wash away the ethanol
2. To soften the leaf
e) Why is the leaf not heated directly on the Bunsen burner?
ANS: Because ethanol easily catches fire
f) What observation would be made when the leaf is finally tested with iodine solution?
ANS: The leaf turns blue black
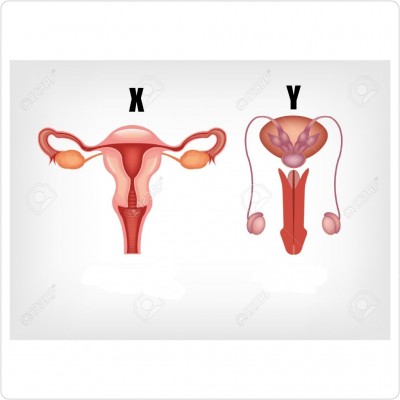
The diagrams shows the reproductive systems of human. Study them carefully and answer the questions below:
a) Identify each of the systems labelled X and Y.
ANS: X-Female reproductive system
Y-Male reproductive system
b) Name the part of X where fertilization occurs.
ANS: Fallopian tube
c) Name the part of Y that produces sperm.
ANS: Testes
d) Which diagram does the following part belong :
(I) ovary, cervix and uterus
(II) urethra, epididymis and scrotum
ANS: (I) diagram X
(II) diagram Y